Agaricus subrufescens (Agaricus Blazei, ABM)
Agaricus subrufescens (A. blazei, ABM) — Materia Medica
Snapshot
Edible medicinal mushroom rich in β-glucans. Used for immune support and healthy inflammatory balance. Common preparations include strong teas/decoctions, powders, and dual-extract approaches (hot water + alcohol).Agaricus subrufescens: The Edible Almond Mushroom
Agaricus subrufescens, also known as the Almond Mushroom, is a unique fungus with remarkable health benefits and culinary uses. This article explores its nutritional profile, medicinal properties, and tips for cultivating it at home.
Key Takeaways
- Agaricus subrufescens, or the Almond Mushroom, offers unique culinary and health benefits, including a sweet almond flavor, high protein content, and various bioactive compounds.
- This mushroom has a complex taxonomic history and is often confused with other species; careful observation of its characteristics aids in accurate identification.
- Research highlights the medicinal potential of Agaricus subrufescens, showing its capacity to boost immune health and inhibit tumor growth, although safety concerns regarding its consumption remain.
Unveiling Agaricus subrufescens: The Almond Mushroom
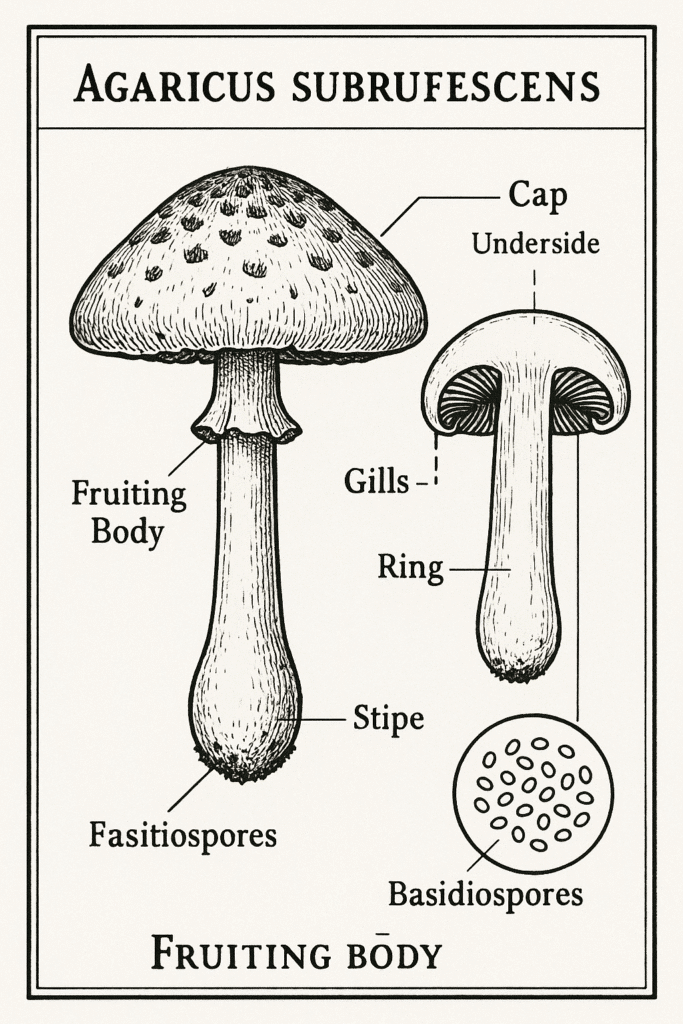
Agaricus subrufescens, or the Almond Mushroom, is a marvel in the world of fungi. Its characteristics include:
- Cap shape: starts out hemispherical before transitioning to a more convex shape
- Cap size: can measure anywhere from 5 to 25 centimeters in diameter
- Gill color changes: from a whitish hue to a pinkish tint, eventually settling into a rich chocolate brown
- Scent: emits a sweet, almond-like fragrance reminiscent of marzipan, making it a notable example of agaricus mushroom and almond agaricus.
This visual transformation and delightful aroma are reasons why it stands out among other mushrooms.
The flavor of Agaricus subrufescens is another aspect that sets it apart. Compared to the common button mushroom, Agaricus bisporus, the Almond Mushroom offers a more pronounced taste, making it a favorite among culinary enthusiasts. Its sweet smell and almond-like taste elevate dishes, providing a unique twist to traditional recipes. Whether sautéed, grilled, or used in soups and stews, this mushroom adds a depth of flavor that is hard to replicate.
Not only is the Almond Mushroom a treat for the senses with its almond taste, but it also holds significant nutritional and medicinal value, including cultivated edible and medicinal benefits, as well as being an edible and medicinal mushroom. Its appeal extends beyond the kitchen, as it has been recognized for its health-boosting properties for generations.
Exploring the world of Agaricus subrufescens and agaricus mushrooms and fungus agaricus blazei reveals why this mushroom has secured a spot in both gourmet kitchens and natural medicine cabinets worldwide.
Taxonomic History and Identification
The story of Agaricus subrufescens begins with its first description by the American mycologist Charles Horton Peck. Identified in the late 19th century, this mushroom was originally described from regions in the Northeastern United States and Canada. Over the years, it has been referred to by several names and has often been confused with other species within the Agaricus genus. However, Agaricus subrufescens maintains taxonomic priority as the oldest name, solidifying its place in mycological records.
Richard Kerrigan undertook genetic and interfertility testing, which played a crucial role in distinguishing Agaricus subrufescens from other similar species. These tests found European samples called, previously referred to by different names, were indeed the same species originally described in North America. This revelation has helped clarify the taxonomy of this remarkable mushroom, ensuring that it is correctly identified and classified in scientific literature.
Differentiating from Similar Species
One of the challenges in mycology is accurately identifying species that share similar characteristics. Taxonomy agaricus subrufescens is no exception, often being mistaken for other Agaricus species such as Agaricus hondensis and Agaricus augustus. The latter, known as “the prince,” is primarily found on the west coast and features distinctive stem decorations that set it apart. Despite these similarities, careful observation of specific traits can aid in accurate identification.
Agaricus species comparison:
- Agaricus subrufescens prefers disturbed ground.
- Agaricus nanaugustus typically grows near spruce trees.
- Agaricus moelleri (inky mushroom) resembles Agaricus subrufescens but has a distinctly different odor and appearance.
Observing these subtle differences helps enthusiasts and mycologists accurately identify this valuable mushroom.
Habitat and Distribution
Agaricus subrufescens is native to North America, where it is commonly found growing in large clusters within leaf litter and nutrient-rich soil. Thriving in these environments highlights its adaptability and resilience. Beyond its native range, this mushroom has been documented in diverse regions across the globe, including:
- California
- Hawaii
- Great Britain
- The Netherlands
- Japan
- The Philippines
- Iran
- Australia
- Brazil
- Uruguay
Such a wide distribution highlights its capacity to adapt to various climates and habitats.
This global presence is a testament to the mushroom’s versatility. Whether in the temperate climates of the eastern United States or the tropical regions of Brazil, the Brazilian fungus, agaricus brasiliensis, manages to flourish. This adaptability not only makes it an intriguing subject for mycologists but also a promising candidate for cultivation in different parts of the world.
Cultivating Agaricus subrufescens at Home
For those interested in mushroom cultivation, Agaricus subrufescens presents an attractive option. Unlike some other varieties that require meticulous growing conditions, the Almond Mushroom is relatively easy to cultivate. A suitable substrate for its growth includes a composted substrate or garden bed, which provides the necessary nutrients for the mushroom to thrive. One bag of sawdust spawn can inoculate an area of 16 square feet, making it a manageable project for home gardeners.
Harvesting is another crucial aspect of mushroom cultivation. For Agaricus subrufescens, it is best to harvest early in the morning or late in the evening to preserve moisture and enhance flavor. Proper harvesting techniques, such as using a knife or a gentle twisting motion, can also help maintain the health of the mycelium, ensuring continued growth and yield.
Best Practices for Garden Compost
High-quality compost is crucial for successful mushroom cultivation. A balanced compost mix, combining kitchen scraps with garden waste, can significantly enhance the substrate’s quality. Adding nitrogen-rich materials like grass clippings can further improve the compost, providing the necessary nutrients for the mushrooms to flourish.
A proper carbon to nitrogen ratio is vital for effective composting. This balance ensures that the compost decomposes efficiently, creating a nutrient-rich environment that supports robust mushroom growth, including the benefits of decomposed plant matter.
Following these best practices allows gardeners to create an optimal substrate for cultivating Agaricus subrufescens.
Summer Harvesting Techniques
Summer is an ideal time for harvesting Agaricus subrufescens. Using a knife to cut the stem cleanly minimizes damage to the mycelium, ensuring that the fungal network remains healthy and productive. Alternatively, a gentle twisting motion can also be effective in removing the mushrooms without harming the underlying mycelium.
Proper harvesting techniques are essential for maximizing yield and maintaining the health of the cultured mycelia. Careful harvesting of the fruit bodies ensures a continuous supply of fresh mushrooms throughout the season. These practices are key to successful mushroom cultivation and can help maintain the longevity of the mushroom bed.
Nutritional Profile and Culinary Uses
Agaricus subrufecens is not only a culinary delight but also a nutritional powerhouse. It has a low fat content, with only 0.5% lipids present in its composition. The fruiting bodies are high in protein, constituting approximately 48% of the total dry matter, making it a valuable addition to a balanced diet.
Rich in vitamins, including various B vitamins and ergosterol, a precursor to vitamin D, Agaricus subrufescens offers numerous health benefits, including reduced lipid peroxidation. Its antioxidant effects and protective and antioxidant effects help protect against oxidative stress, adding to its appeal as a health food, particularly in the form of agaricus supplement products.
Culinary versatility further enhances its value, as it can be used in a variety of dishes to enhance both flavor and nutritional content.
Medicinal Properties and Health Benefits
Agaricus subrufescens is celebrated not only for its culinary uses but also for its profound medicinal properties. It contains significant amounts of bioactive compounds, such as polysaccharides, which contribute to its health benefits. These compounds are known for their therapeutic effects, including immune system stimulation and potential anti-cancer properties.
Research has shown that Agaricus subrufescens can enhance immune health through its bioactive compounds, making it a valuable addition to alternative and complementary medicine. Its ability to combat various diseases through immune modulation highlights its potential as a medicinal mushroom.
Immunomodulating Bioactive Compounds
The bioactive compounds in Agaricus subrufescens, particularly polysaccharides like β-glucans, are essential for enhancing immune responses. These polysaccharides modulate immune system activity, helping to boost the body’s defenses against infections and diseases.
Research indicates that these bioactive compounds can play a significant role in cancer treatment by enhancing immune response and inhibiting tumor growth. The presence of such compounds underscores the medicinal mushrooms’ purported medicinal properties as a powerful medicinal agent in alternative medicine.
Potential Anti-Cancer Effects
Preliminary studies have shown that extracts from Agaricus subrufescens can inhibit tumor growth, suggesting disease treatment as a promising supplementary approach alongside conventional cancer therapies. Research indicates that these abm extract may reduce tumor growth and exhibit anti-tumor activity in various cancer models, supporting the findings of toxicity preliminary research.
Polysaccharides extracted from the mushroom play a significant role in preventing tumor metastasis and reducing tumor size in animal models. Additionally, ergosterol found in Agaricus subrufescens has been linked to anti-tumor activity, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic agent in cancer treatments.
Hepatoprotective Effects
Agaricus subrufescens also offers protective benefits for liver health. Research suggests that its extracts can protect liver cells from damage caused by harmful substances, improving liver function overall, which leads to improved liver function.
Studies have shown that the mushroom can significantly reduce serum liver enzyme levels, indicating improved liver function and a protective effect against liver damage. This hepatoprotective property makes Agaricus subrufescens a valuable addition to natural health remedies for supporting liver enzymes function.
Safety and Toxicity Concerns
While Agaricus subrufescens is generally recognized as edible, its safety profile has not been thoroughly evaluated. Consumers should approach its consumption with caution due to insufficient data on its long-term safety.
The presence of agaritine, a compound found in Agaricus subrufescens, has raised concerns due to its potential mutagenic properties. Overall, the consumption of this mushroom presents safety concerns and potential toxicity that warrant further research.
Integrative Cancer Therapies Using Agaricus subrufescens
Agaricus subrufescens holds significant promise in integrative cancer therapies due to its bioactive compounds. Studies have shown that its extracts can contribute to tumor growth suppression in various animal models, enhancing the efficacy of existing chemotherapeutic agents when used in conjunction.
Compounds such as ergosterol and agaritine from Agaricus subrufescens have demonstrated specific anti-tumor activities against certain cancer cells. The mushroom’s ability to stimulate apoptosis in cancer cells while sparing normal cells highlights its potential as a therapeutic agent in cancer treatments.
Summary
Agaricus subrufescens, the Almond Mushroom, is a remarkable fungus that combines culinary delight with profound health benefits. From its unique aroma and flavor to its potential in enhancing immune function and combating cancer, this mushroom stands out as a valuable addition to both kitchens and natural medicine cabinets. As research continues to uncover its full potential, Agaricus subrufescens promises to remain a subject of fascination and admiration.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best way to cultivate Agaricus subrufescens at home?
The best way to cultivate Agaricus subrufescens at home is to use a composted substrate or garden bed and inoculate it with sawdust spawn. For optimal results, harvest in the early morning or late evening to ensure moisture and flavor retention.
What are the key health benefits of Agaricus subrufescens?
Agaricus subrufescens is beneficial for enhancing immune function, exhibiting potential anti-cancer properties, and providing protective benefits for liver health. Incorporating it into your diet may support overall wellness.
How can I differentiate Agaricus subrufescens from similar species?
To differentiate Agaricus subrufescens, look for its unique sweet almond-like aroma, the way its gill color changes, and its specific habitat preferences. These characteristics set it apart from similar species.
Are there any safety concerns with consuming Agaricus subrufescens?
Yes, consuming Agaricus subrufescens poses safety concerns due to the presence of agaritine, which may have mutagenic effects, and its long-term safety has not been well established.
Can Agaricus subrufescens be used in cancer treatment?
Agaricus subrufescens shows promise in cancer treatment, as preliminary studies indicate its extracts may inhibit tumor growth and improve the effectiveness of chemotherapy. Its potential as part of integrative cancer therapies is notable.
Identification & Harvest
Preparations
- decoction
- tincture
- powder
- capsule
Safety
Generally well tolerated as food; monitor for mushroom allergies and interactions with immunomodulating therapies.Related Research
References
- (2019) Overview of β-glucans in Agaricus
- (2021) Modern perspectives on Agaricus subrufescens
Educational content only; not medical advice.
