Alfalfa
Medicago sativa — Materia Medica
Snapshot
Nutrient-dense legume used traditionally as a nutritive/alterative. Aerial parts supply minerals and vitamins (notably vitamin K), chlorophyll, and saponins; typically prepared as an infusion, powders, or capsules. Sprouted seeds are commonly eaten as food. Clinical evidence for lipid/glucose effects is limited and mixed; primary use remains nutritional support.Alfalfa (Medicago sativa, a.k.a. lucerne) is a classic nutritive and alterative herb. The aerial parts are rich in minerals and vitamins (notably vitamin K) and are taken as infusions, powders, or capsules; the sprouted seeds are a common food. Evidence for lipid or glucose effects is limited and mixed, so herbal use centers on gentle nutritional support rather than targeted therapy.
Safety: Because of vitamin K, alfalfa leaf can oppose warfarin and similar anticoagulants. Isolated reports link high-intake seed/sprout products (L-canavanine content) with flares in autoimmune conditions—choose leaf products and avoid high-dose seed supplements if concerned. Not for infants.
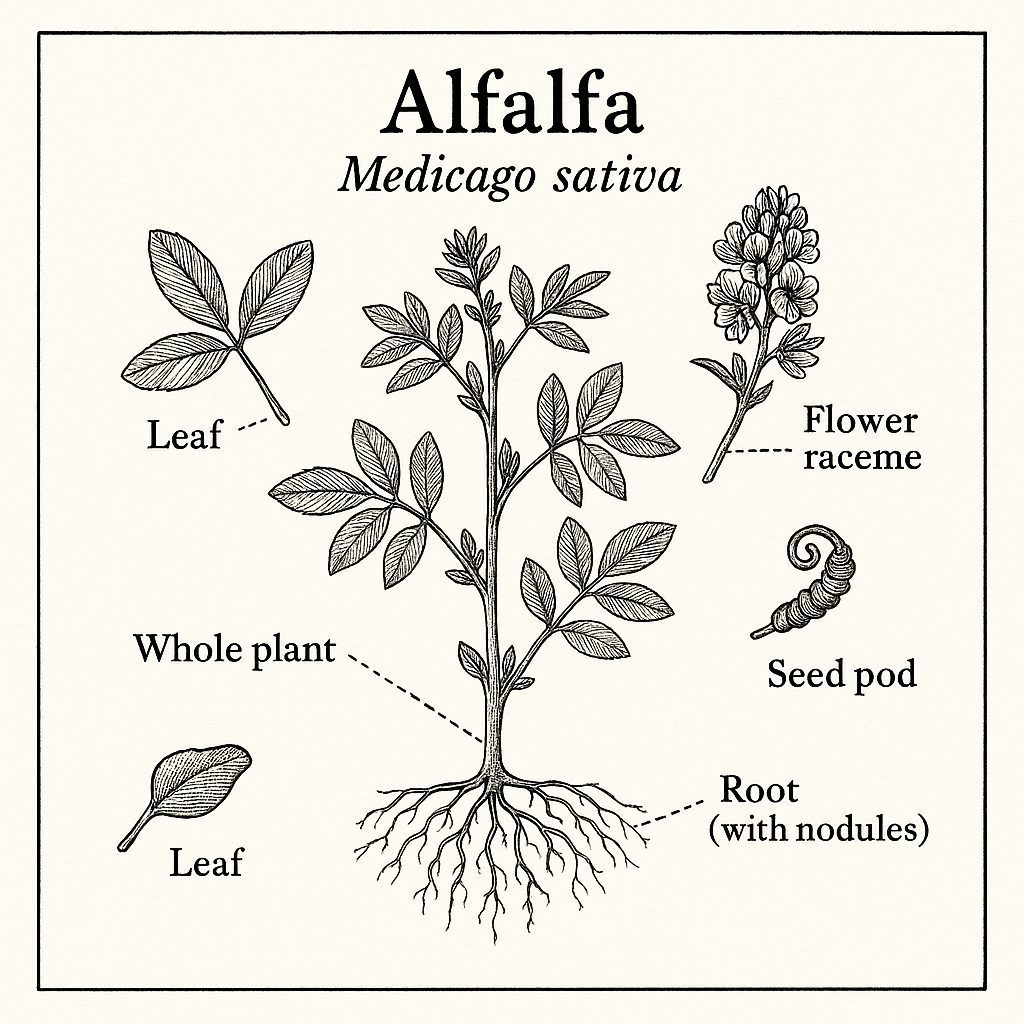
Identification & Harvest
Use clean, properly dried leaf. If consuming sprouts, source from reputable producers and handle with strict food-safety hygiene.Preparations
- tea-infusion
- tincture
- powder
- capsule
Safety
Avoid if taking warfarin or other vitamin-K–antagonist anticoagulants (alfalfa leaf is vitamin-K–rich). Use caution with autoimmune conditions (isolated reports of L-canavanine in SEEDS/SPROUTS exacerbating lupus-like symptoms); prefer leaf products and avoid high-dose seed supplements in such cases. Sprouts can carry food-borne pathogens—follow food-safety guidance and avoid raw sprouts in pregnancy, for young children, older adults, or immunocompromised individuals. Possible GI upset in sensitive users. Not for infants.Related Research
No studies yet.
References
- (2022) Memorial Sloan Kettering — About Herbs: Alfalfa (Medicago sativa)
- (2024) USDA NRCS PLANTS Database: Medicago sativa profile
- (2013) AHPA Botanical Safety Handbook, 2nd ed. (American Herbal Products Association)
- (2005) Mills S, Bone K. The Essential Guide to Herbal Safety (Churchill Livingstone)
- (2003) Hoffmann D. Medical Herbalism: The Science and Practice of Herbal Medicine (Healing Arts Press)
- (2007) PDR for Herbal Medicines, 4th ed. (Thomson/Medical Economics)
- (2001) Brinker F. Herb Contraindications and Drug Interactions, 3rd ed.
- (2009) Tilgner S. Herbal Medicine from the Heart of the Earth, 2nd ed.
- (2008) Wood M. The Earthwise Herbal: A Complete Guide to Old World Medicinal Plants
Educational content only; not medical advice.
