Phyllanthus emblica Amla
Phyllanthus emblica L. — Materia Medica
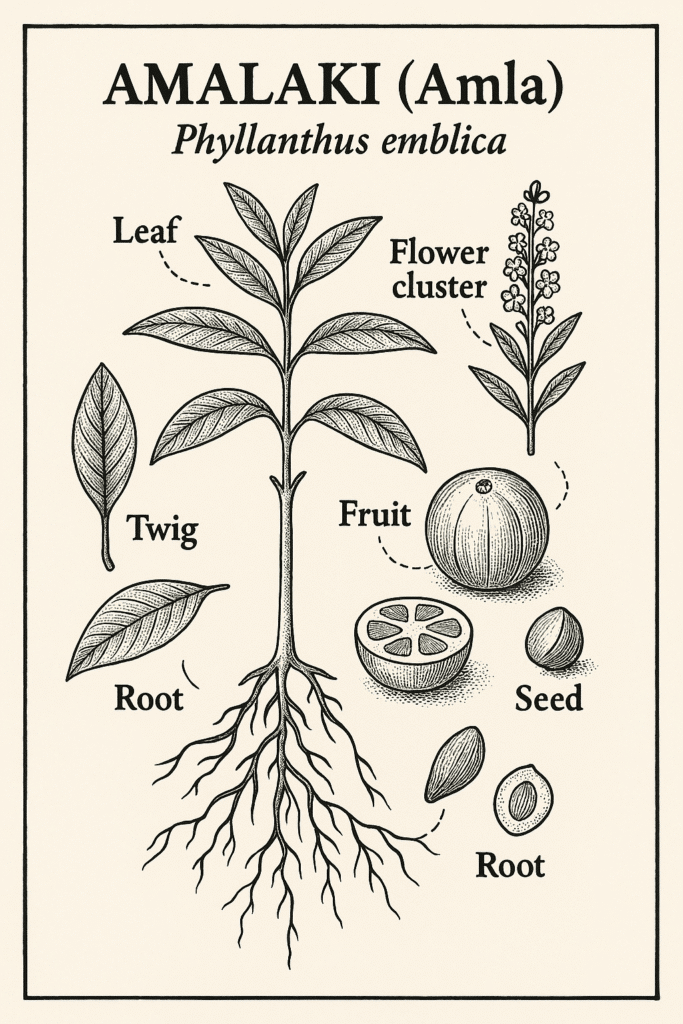
Snapshot
Widely consumed fruit rich in vitamin C, polyphenols (tannins like emblicanin) and other antioxidants. Traditional ‘rasayana’ (rejuvenative) in Ayurveda. Modern evidence includes small clinical studies of standardized amla fruit extracts on lipids, glycemic markers, and oxidative stress; results are promising but heterogenous and dose/form dependent. Food-level use is well established; concentrated extracts vary by manufacturer—avoid disease claims.Amalaki (Amla) (Phyllanthus emblica (Emblica officinalis)).
Parts usedFruit
PreparationsPowder; decoction; chyawanprash; tincture.
Primary actionsAntioxidant; rasayana (Ayurvedic rejuvenative); mild laxative
SystemsDigestive; Immune
NotesSour, tannic fruit central to Ayurveda (amalaki). Rich in tannins and vitamin‑C equivalents.
Used as a daily rejuvenative and for gentle digestive regularity. Key component of chyawanprash.
Identification & Harvest
Small to medium deciduous tree; branchlets with many simple leaves; fruits are pale green–yellow, firm, globose berries with 6 vertical grooves. Harvest mature fruits when fully sized yet still firm. For drying, use gentle heat to preserve constituents; powder from dried fruit is a common form. Classic blend: Triphala (with Terminalia chebula & T. bellirica).Preparations
- tea-infusion
- decoction
- tincture
- glycerite
- powder
- syrup
- capsule
Safety
Generally well tolerated as a food. Possible GI upset in sensitive individuals (tannins/acid). Caution with antidiabetic medication (may enhance glucose-lowering) and with anticoagulant/antiplatelet therapy (theoretical additive effects). Insufficient safety data in pregnancy/lactation above typical dietary amounts—use food amounts only. Ensure quality sourcing (proper identity; avoid adulteration).Related Research
No studies yet.
References
- (2001) Ayurvedic Pharmacopoeia of India – Amalaki (Phyllanthus emblica) monograph
- (2011) Pharmacognosy review of Emblica officinalis (Amla)
- (2012) Human studies of amla extract on lipids and oxidative stress (clinical summaries)
- (2010) Traditional rasayana uses of Amalaki (Ayurveda texts overview)
Educational content only; not medical advice.
